- Docker For Windows And Virtualbox
- Docker For Windows Vs Virtualbox
- Docker For Windows And Virtualbox Usb
By Al Crowley, TCG Principal Engineer
Docker supports Docker Desktop on Windows for those versions of Windows 10 that are still within Microsoft’s servicing timeline. What’s included in the installer The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Notary, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper. For Windows 7 (and higher) users, Docker provides Docker Toolbox, an installer that includes everything needed to configure and launch a Docker environment. Docker Toolbox allows you to deploy development containers in legacy Windows systems that do not meet the requirements of the new Docker for Windows application. Dec 12, 2017 To install Docker on Windows, you can’t install the regular and new Docker for Windows, because you have Virtual Box installed! Docker for Windows requires Hyper-V to work. VirtualBox does. Oct 21, 2019 If you’ve ever tried to install Docker for Windows, you’ve probably came to realize that the installer won’t run on Windows 10 Home.Only Windows Pro, Enterprise or Education support Docker.
Running Docker containers on a Windows 10 PC has been difficult for the last few years. It’s even more difficult if you want to run VirtualBox virtual machines (VM) at the same time. A casual Google search will turn up droves of postings saying that you absolutely can not do both at once.
The problem is that Docker on Windows required you to enable the Hyper‑V hypervisor but VirtualBox 5.x will not run while Hype‑V is active. The docker+VM on Windows OS question has been asked and answered so many times over the years that search results are flooded with the same outdated answer: No, you can’t have both. For some of us, this gets further complicated by people saying you can’t even use Hyper‑V at all on the Windows 10 Home version. Well, things are changing — but you have to really dig deep on the web to get the info you need to make it happen.
Two recent changes have turned things around. First, VirtualBox 6 has an ‘experimental’ support for Hyper‑V. Second, the upcoming Windows Subsystem for Linux version 2 fully supports docker using Hyper‑V, even on Windows Home edition.
WSL2
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is really great for developers who want to install Windows on their PC. It allows you to install a Linux as a peer operating system to Windows that you can easily access through a Linux terminal. WSL version 1 did have some limitations though. A big one for me is that the system call emulation layer Microsoft provides could not support Docker.
Jul 25, 2016 Installing Docker for Windows enables Hyper-V, which prevents you from being able to use VMWare Workstation or Player. In the future, I would like to see Docker for Windows be able to specify which Virtualization platform to use, Hyper V, VirtualBox or VMWare. I know that I could continue to use Docker Toolbox, but that is not the same on.
WSL2 is big update—faster file system, support for directly running the Linux kernel on Hyper‑V. It is scheduled for the “20H1” update that will be released in the spring of 2020—but you can get it now if you join the Windows Insider program. Instructions for that are found in the Windows Insider Program User Guide. Once you have an updated version of Windows, install of WSL2 is easy enough if you follow the instructions on Microsoft’s website.
VirtualBox 6
Installing VirtualBox 6 is simple and you can find the install on the VirtualBox download page. It can be a little tricky to get some VMs running now that you have Hyper‑V enabled. For me, when I tried to restart an old VM, or create a new one using the defaults, I would get an error right away.
To get your VMs working, you will need to go into the VM settings, choose the System section, go into the Acceleration tab, and select Hyper‑V as the Paravirtualization Interface. You may also have to disable the I/O APC checkbox on the Motherboard tab. I’ve found some guest OS crash with it checked, but if it works for you, then leave it as is. THEN, you need to add an obscure setting to the .vbox file associated with your VM image:

I found that tip about the UseRing0Runloop setting on a forum posting that I was lucky enough to stumble upon.
Performance/Stability
This is working for my setup. Running with these beta test level features does have a few downsides. The VirtualBox VM performance is noticeably slower running this way. It is also a little unstable and you will get intermittent guest OS crashing that you didn’t have before. That’s ok for me since I’m using this for development work so it’s easy enough to restart the VM when it happens. On the WSL side, version 2 is a big improvement. Anything that touches the filesystem is much, much faster. Then we have Docker support, of course, which is why I went through all this in the first place. Unfortunately, I am seeing that some base container images will crash on Docker. I’ve found Centos to be problematic, but Ubuntu works without a problem. Microsoft is still working on WSL2 and judging by the forums, container support is getting better.
This is most definitely not a good fit for most people, but for me, this is an improvement over my old setup. The instability is a little annoying at times. As of right now, January 2020, every component is still in development: Fast ring Insider version of Windows 10, beta version of WSL2, and experimental support for Hyper‑V in VirtualBox. With that said, I’ve been able to do things with Docker containers and WSL that were just not possible a few months ago—and I really like that.
Why Docker?
Docker is an open platform that can be used to deploy applications in isolated, secure containers. Docker containers are lightweight, simple to configure and work consistently in diverse IT environments. Most Bitnami applications are available as Docker containers and offer all the usual Bitnami benefits: security, optimization, consistency and frequent updates.
Install Docker Toolbox in Windows
For Windows 7 (and higher) users, Docker provides Docker Toolbox, an installer that includes everything needed to configure and launch a Docker environment. Docker Toolbox allows you to deploy development containers in legacy Windows systems that do not meet the requirements of the new Docker for Windows application.
Docker Toolbox contains the following tools:
- Docker Machine
- Docker Engine
- Docker Compose
- Kinematic
- Docker Quickstart Terminal App
- Oracle VirtualBox
Prerequisites
Your Windows system must meet the following minimum requirements:
Docker For Windows And Virtualbox
- 64-bit Windows 7 (or higher)
- Virtualization enabled
Step 1: Check system configuration
The first step is to check if your system configuration meets the requirements needed for running the installer successfully.
Check Windows version
Docker Toolbox requires 64-bit Windows 7 (or higher). There are many ways to verify if your machine meets these requirements.
Check OS version in Windows 10
- Type “Settings” in the Windows Search Box and select “System -> About”.
- Find your Edition and Version under your PC name.
- Look “System type” to check if you are running a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
Check OS version in Windows 7 and 8
- Go to “Control Panel -> System and Security -> System”. Check the Windows Edition and System Type.
Find more information about how to check your Windows operating system.
Enable hardware-assisted virtualization
Enabling hardware-assisted virtualization is mandatory for installing Docker Toolbox.
Hardware-assisted virtualization in Windows 8 or higher
You can check if your system supports this technology in two different ways.
Using the Windows Task Manager:
- Type “Task Manager” in the Windows Search Box.
- Click “Performance” tab. Look under “CPU” to find out if virtualization is enabled or not.
Using the Windows Command Prompt:
Type “Command Prompt” in the Windows Search Box.
Right-click to open the options menu. Select “Run as administrator”.
Navigate to the C: drive by typing:
Run the following command:
NOTE: If virtualization is not enabled in your machine, please check how to enable it in your BIOS by following your manufacturer’s instructions.
Hardware-assisted virtualization in Windows 7
- Download and run the Microsoft Hardware-Assisted Virtualization Detection Tool.
Step 2: Install Docker Toolbox
Download Docker Toolbox
Once the system requirements have been verified, download the installer from the Docker website. Click the download button with the Windows logo.
NOTE: Make sure that you are installing the latest release of Docker Toolbox. Find the list of releases in Docker’s GitHub repository.
Docker Toolbox will install the following applications:
- Docker Client for Windows
- Docker Toolbox management tool and ISO
- Oracle VirtualBox
- Git MSYS-git UNIX tools
Launch the Docker Toolbox setup wizard
IMPORTANT: If you have VirtualBox installed and running, please shut down it before the installation begins.
These are the steps you must follow for completing the Docker Toolbox installation:
Open the installer by double-clicking the .exe file. Choose “Yes” in the Windows security dialog box to allow the program to make changes to your PC.
When the Docker Toolbox setup wizard starts, click the “Next” button.
Choose the local folder for Docker Toolbox installation. Click the “Next” button.
Check the components to be installed (“Git for Windows” is recommended; uncheck “VirtualBox” if already installed). Click “Next”.
Accept all default options and click the “Next” button.
Verify that all selected components will be installed. Click “Back” to change any settings.
Click the “Install” button to finish the installation. If Windows should ask you about permitting changes to your PC, click “Yes” to allow it to make the necessary changes.
After all the components are installed, the wizard will notify that installation was successful. Uncheck “View Shortcuts in File Explorer” and click “Finish”.
Step 3: Verify the installation
To verify installation, follow these steps:
Go to your desktop, which should have these three icons:
- Docker Quickstart Terminal
- Kitematic
- Oracle VM VirtualBox.
Launch the Docker Quickstart Terminal by clicking the corresponding icon. This starts the creation of the Docker machine and all its components.
Click near the $ symbol to activate the terminal.
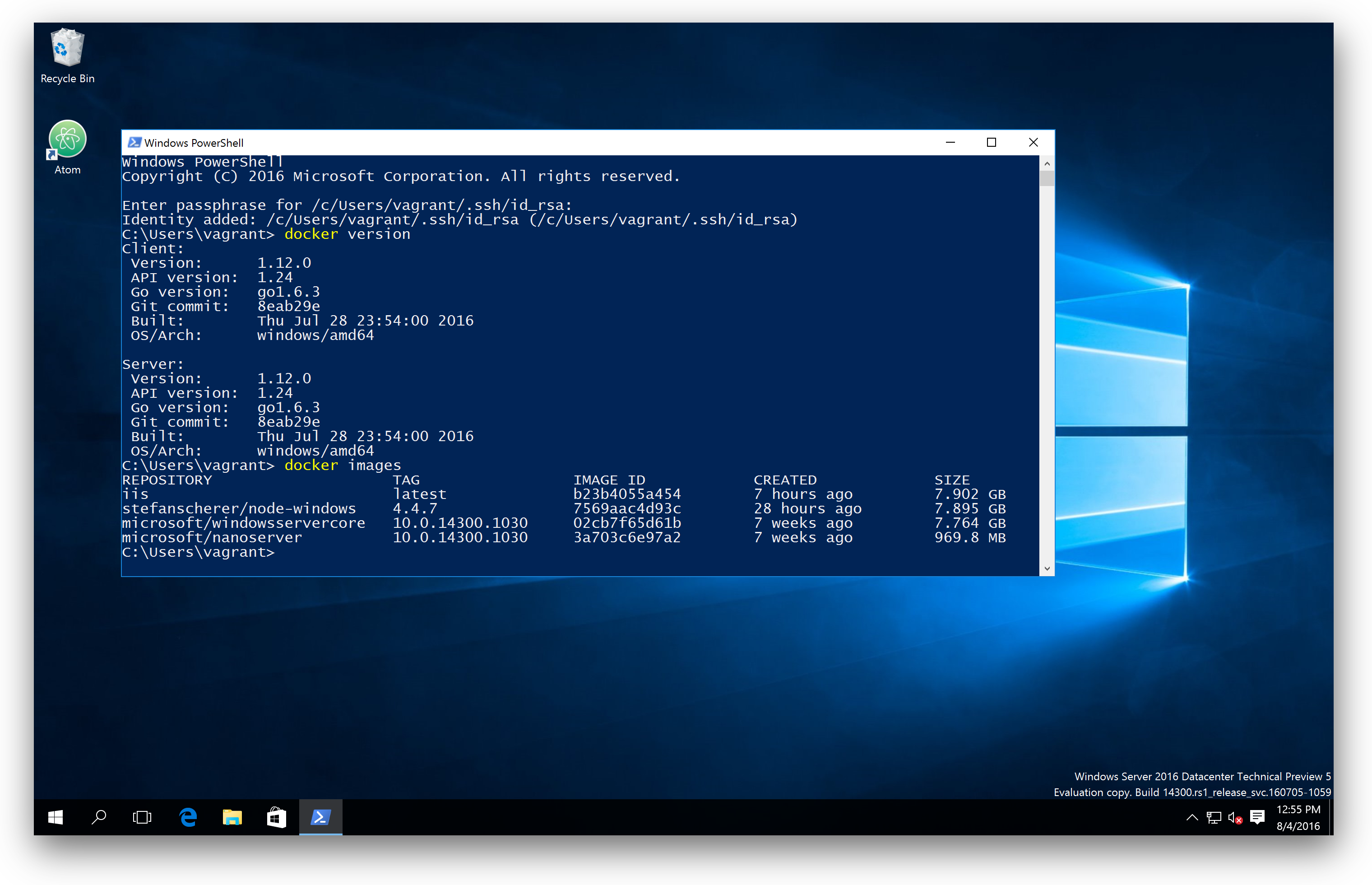
Type the following command and press Enter:
Docker will download and run the “Hello world” container. A confirmation message will be displayed in the terminal.
This indicates that your Docker installation is successful.
Step 4: Run Bitnami WordPress in Docker
Now that Docker is running, the next step is to use it with a Bitnami application. This guide will use the Bitnami WordPress Docker image.
The Bitnami WordPress Docker image provides the latest version of WordPress, including recent updates.This image deploys two containers, one for the database and another for the application itself.
Follow the steps below to deploy the Bitnami WordPress image:
Docker For Windows Vs Virtualbox
Open the Docker Quickstart Terminal by double-clicking the icon.
Browse to Bitnami’s Docker image for WordPress. Click the “Clone or download” button. Copy the URL to the clipboard.
Type git clone in the Docker Quickstart Terminal and paste the URL:
Check the IP address of your Docker machine by executing the following command:
Change the directory:
Run the docker-compose up command to launch the containers and to create the volumes:
Access the application by browsing to the Docker machine IP address. You should see something like this:
Docker For Windows And Virtualbox Usb
Useful links
